Building Travel Agent with OpenAI Agents SDK
Check Out: https://app.langdb.ai/sharing/threads/43cfa16f-042e-44ca-ad21-06f52afeca39
Code
This guide illustrates how to build a multi-agent travel query workflow using the OpenAI Agents SDK, augmented by LangDB for guardrails, virtual MCP servers (tool integration), and model routing.
OpenAI introduced the Agents SDK, a lightweight, Python-first toolkit for building agentic AI apps. It’s built around three primitives:
- Agents: LLMs paired with tools and instructions to complete tasks autonomously.
- Handoffs: Let agents delegate tasks to other agents.
- Guardrails: Validate inputs/outputs to keep workflows safe and reliable.
Overview
This guide illustrates how to build a multi-agent travel query workflow using the OpenAI Agents SDK, augmented by LangDB for advanced tracing, tool integration, and model routing.
We will create a 4-agent pipeline:
- Query Router Agent: Routes user queries to the appropriate specialist agent.
- Booking Specialist: Manages booking-related requests.
- Travel Recommendation Specialist: Provides destination recommendations with web search support.
- Reply Agent: Formats the final output for the user.
Installation
pip install openai-agent 'pylangdb[openai]' python-dotenv
Environment Variables
export LANGDB_API_KEY="<your_langdb_api_key>"
export LANGDB_PROJECT_ID="<your_langdb_project_id>"
export LANGDB_API_BASE_URL="https://api.us-east-1.langdb.ai"
Code Walkthrough
The snippets below break down how to configure the OpenAI Agents SDK with LangDB for end-to-end tracing and custom model routing.
Initialize LangDB Tracing
First, initialize pylangdb tracing. This must be the first step to ensure all subsequent SDK operations are captured.
import os
import asyncio
import uuid
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from pylangdb.openai import init
# Load environment variables and initialize tracing
load_dotenv()
init()
Configure the OpenAI Client & Model Provider
Next, configure the AsyncOpenAI client to send all requests through the LangDB gateway. We then create a CustomModelProvider to ensure the Agents SDK uses this client for all model calls.
from agents import (
Agent, Runner, set_default_openai_client, RunConfig,
ModelProvider, Model, OpenAIChatCompletionsModel
)
from openai import AsyncOpenAI
# Configure the client with LangDB headers
client = AsyncOpenAI(
api_key=os.environ["LANGDB_API_KEY"],
base_url=os.environ["LANGDB_API_BASE_URL"],
default_headers={"x-project-id": os.environ["LANGDB_PROJECT_ID"]}
)
# Set the configured client as default for tracing
set_default_openai_client(client, use_for_tracing=True)
# Create a custom model provider to route all model calls through LangDB
def get_model(model_name):
return OpenAIChatCompletionsModel(model=model_name, openai_client=client)
Define the Agents
Now, define the specialist agents and the router agent that orchestrates them. The model parameter can be any model available in LangDB, including the virtual models we configure in the next section.
# Define specialist agents
booking_agent = Agent(
name="Booking Specialist",
instructions="You are a booking specialist. You help customers with their booking and reservation questions.",
model=get_model("openai/gpt-4o-mini")
)
travel_recommendation_agent = Agent(
name="Travel Recommendation Specialist",
instructions="You are a travel recommendation specialist. You help customers find ideal destinations and travel plans.",
model=get_model("langdb/recc_8ac7wclb") # A virtual model with search tools attached
)
reply_agent = Agent(
name="Reply Agent",
instructions="You reply to the user's query and make it more informal by adding emojis.",
model=get_model("langdb/reply_idzqgtrm") # A virtual model for formatting
)
# Define the orchestrator agent
query_router_agent = Agent(
name="Query Router",
instructions="You determine which specialist to use based on the user's query, then hand off to the reply agent.",
model=get_model("langdb/router_c77w2sji"), # A virtual model for routing
handoffs=[reply_agent],
tools=[
booking_agent.as_tool(
tool_name="booking_tool",
tool_description="Use for questions about flight bookings or reservations.",
),
travel_recommendation_agent.as_tool(
tool_name="travel_tool",
tool_description="Use for travel destination recommendations or planning.",
)
]
)
Run the Workflow
Finally, use the Runner to execute the workflow. We inject our CustomModelProvider and a group_id into the RunConfig to ensure all steps are routed through LangDB and linked in the same trace.
async def run_travel_agent(query: str):
group_id = str(uuid.uuid4()) # Links all steps in this session
response = await Runner.run(
query_router_agent,
input=query,
run_config=RunConfig(
model_provider=CUSTOM_MODEL_PROVIDER,
group_id=group_id
)
)
print(response.final_output)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(run_travel_agent("I want to book a flight to Paris."))
Configuring MCPs, Guardrails, and Models
To empower agents with tools like web search or to enforce specific behaviors with guardrails, you use LangDB Virtual Models. This allows you to attach functionality directly to a model identifier without changing your agent code.
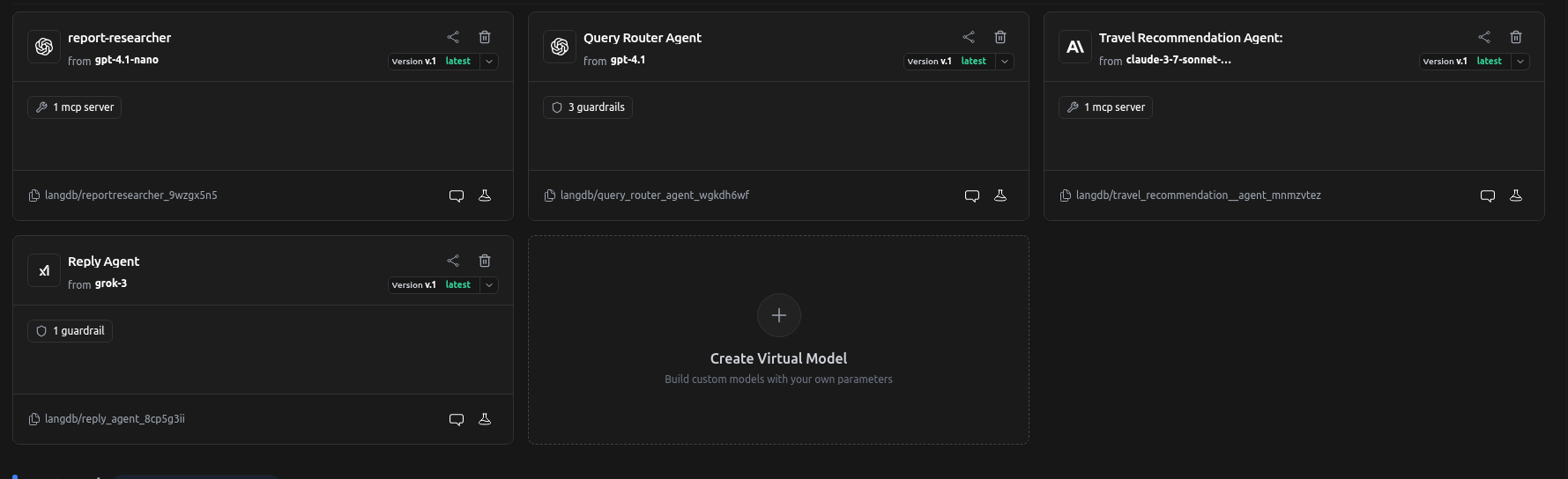
- In the LangDB UI, navigate to Models → + New Virtual Model.
- Create virtual models for your agents (e.g.,
travel-recommender,query-router). - Attach tools and guardrails as needed:
- For the
travel_recommendation_agent: Attach an MCP Server (like Tavily Search) to give it live web search capabilities. - For the
query_router_agent: Attach guardrails to validate incoming requests. For example:- Topic Adherence: Ensure the query is travel-related.
- OpenAI Moderation: Block harmful or disallowed content.
- Minimum Word Count: Reject overly short or vague queries.
- For the
reply_agent: Attach a Language Validator guardrail to ensure the final output is in the expected language.
- For the
- Use the virtual model's identifier (e.g.,
langdb/travel-recommender) as themodelstring in yourAgentdefinition.
Full Trace
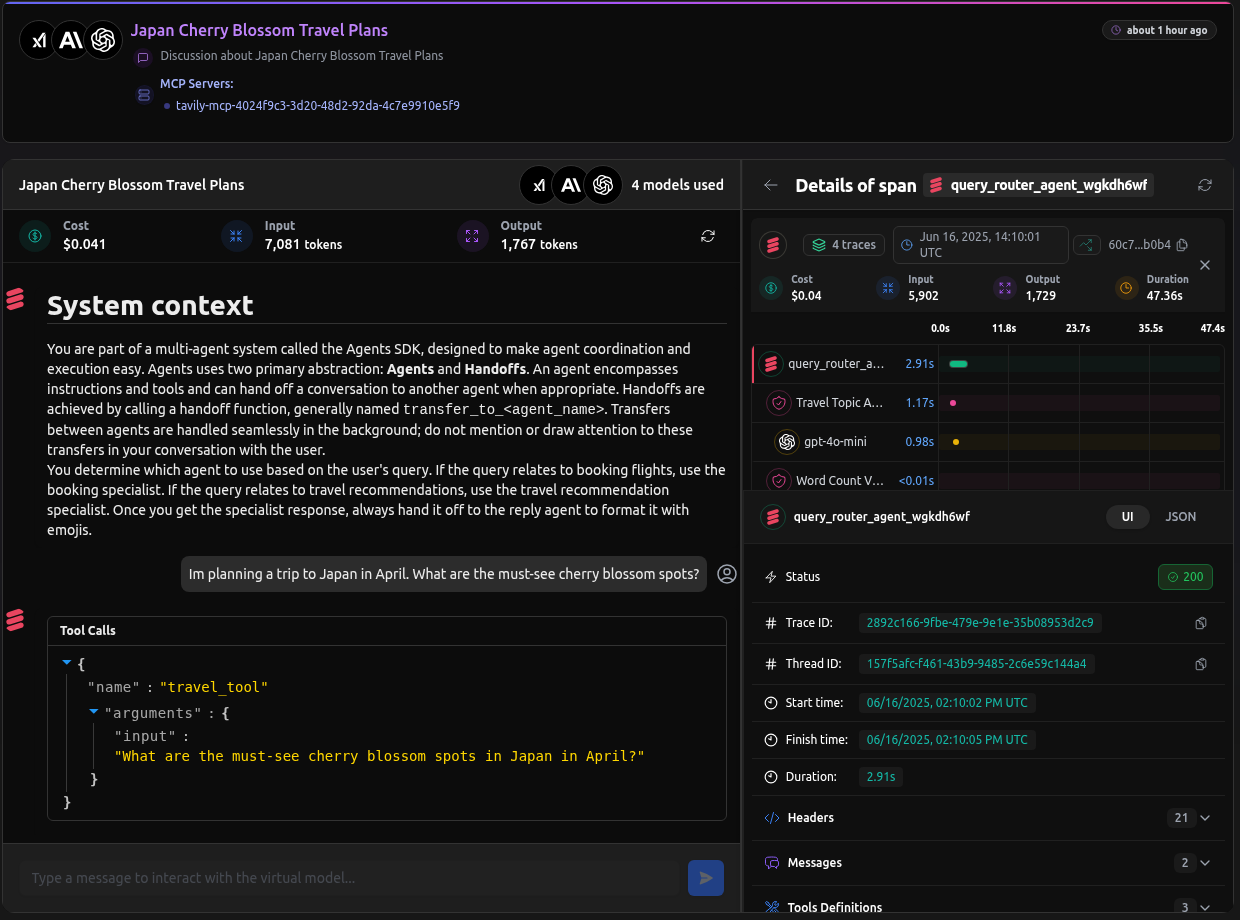
After setting up the virtual models and running the query like:
uv run app.py 'Im planning a trip to Japan in April. What are the must-see cherry blossom spots?'
We get the following trace
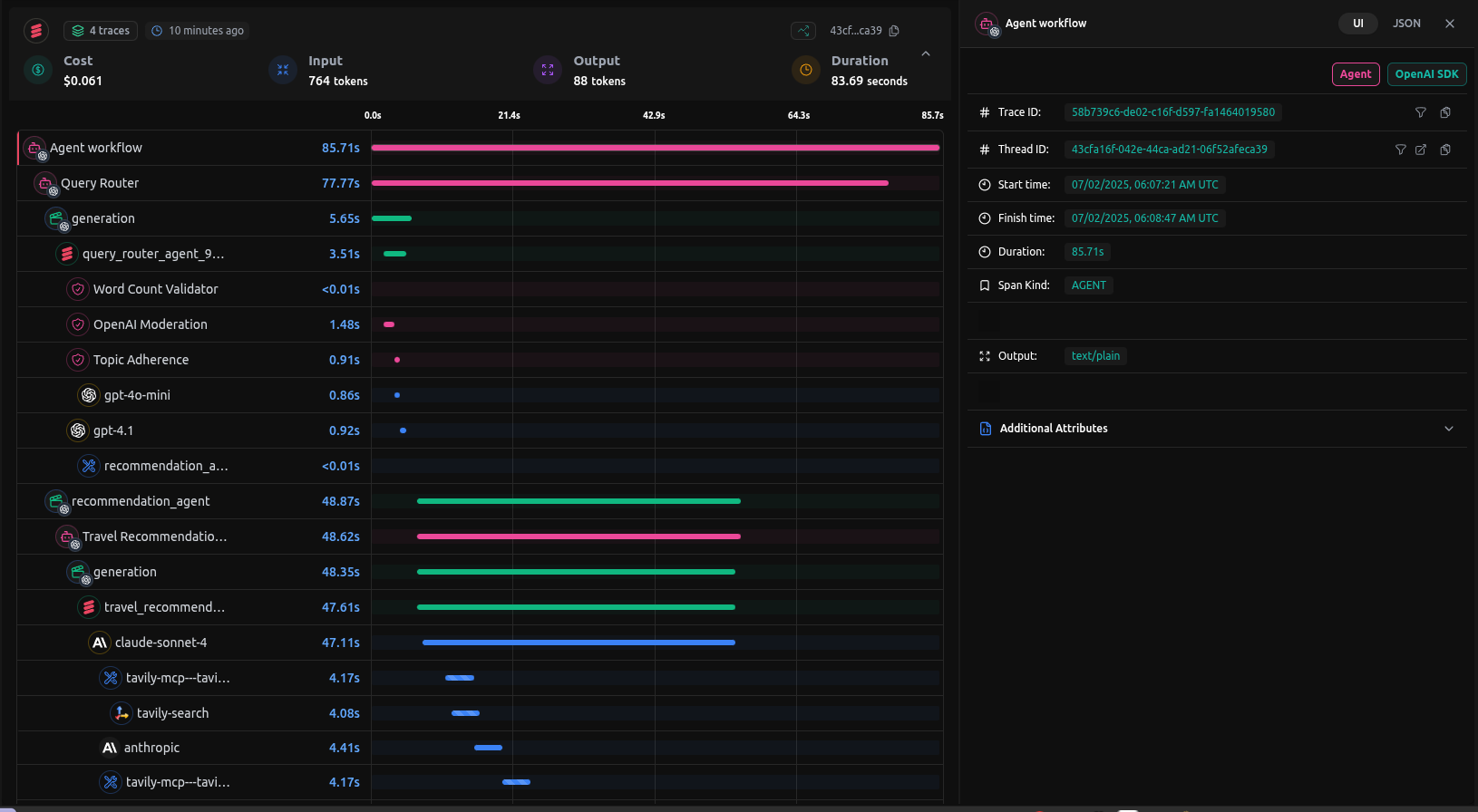
You can check out the entire trace here: